In this use case we build a workflow in which we work with regular expressions to identify the incoming call origin.
- We want to distinguish incoming external calls from incoming internal calls so that we can route to different teams accordingly
- This can be combined with a priority scenario, where we priorize external calls over interal calls
PRECONDITIONS
- You require service owner rights to create the workflow.
Show Icon Legend
| 💡 = A hint to signal learnings, improvements or useful information in context. | 🔍 = Info points out essential notes or related page in context. |
| ☝ = Notifies you about fallacies and tricky parts that help avoid problems. | 🤔 = Asks and answers common questions and troubleshooting points. |
| ❌ = Warns you of actions with irreversible / data-destructive consequence. | ✅ = Intructs you to perform a certain (prerequired) action to complete a related step. |
How to identify the call origin
In Nimbus we can make use of a powerful workflow activity called "Check Parameter". The activity has access to system internal context fields and parameters as well as user-customizable parameters that can be filled during the lifetime of a call using Power Automate flows.
For this use case it is sufficient to validate system parameters. Here is a table of what values to expect during different call origins, in this example assuming that our company's tenant domain is "lunifico.com" and our company's main phone number is +41 58 404 28 00 , whilst direct numbers of our employees are i.e. +41 58 404 28 44 or +41 58 404 28 12
| Call Origin | Value | Check Parameter Activity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calling from | MicrosoftCallId | CallerId | CallerUPN | Validation On Parameter | Regular Expression |
| Internal PSTN | +41584042844 | NULL | NULL | MicrosoftCallerId | ^\+415840428\d{1,2}$ |
| External PSTN | +37553452843 | NULL | NULL | MicrosoftCallerId |
^\+[1-9]\d{1,14}$ This matches all PSTN E.163 numbers. We do not exclude internal number here. |
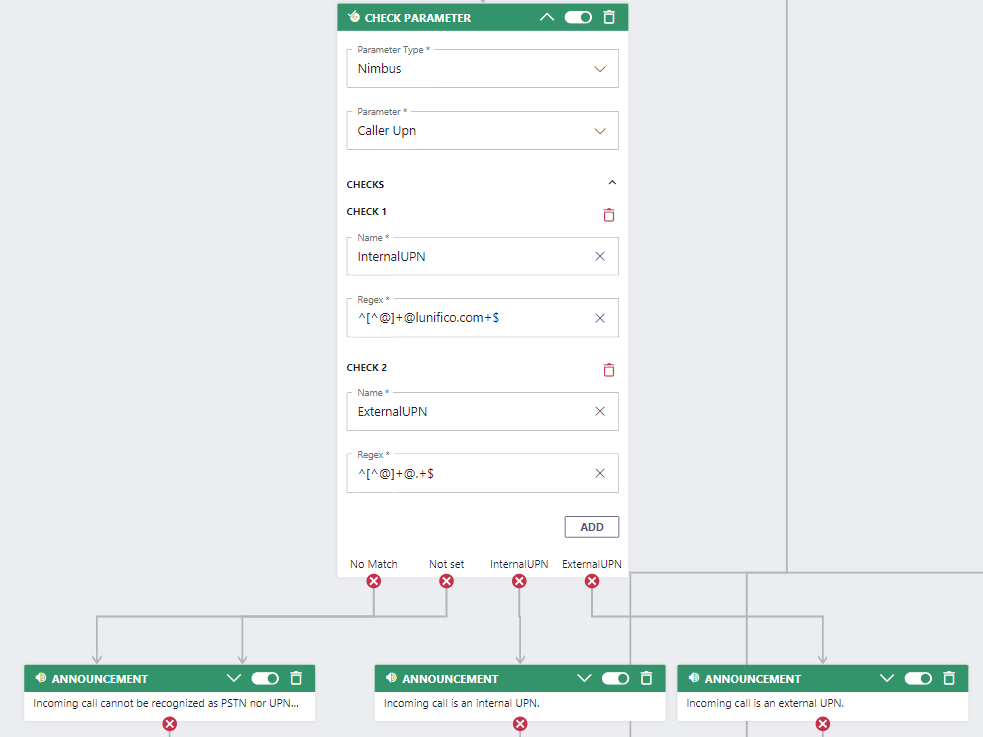
| Internal UPN | f36ef92c-4dad-454e-9d86-bcd334ac864e | f36ef92c-4dad-454e-9d86-bcd334ac864e | mwinter@lunifico.com | CallerUPN | ^[^@]+@lunifico.com+$ |
| External UPN | 1c127f30-0740-4d50-bab1-1ed51d359e06 | 1c127f30-0740-4d50-bab1-1ed51d359e06 | sales@luware.com | CallerUPN |
^[^@]+@.+$ This matches all UPN's. We do not exclude internal UPN's here. |
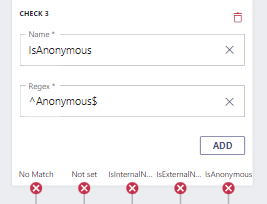
| Anonymous | Anonymous | NULL | NULL | MicrosoftCallerId | ^Anonymous$ |
With this schema in mind we can create our workflow.
Creating the workflow
Now we can start building the Workflow. 💡 In our example below we focus on the validation. Once you know the origin of the call, you can freely choose the following actions after that
Overview of the workflow...
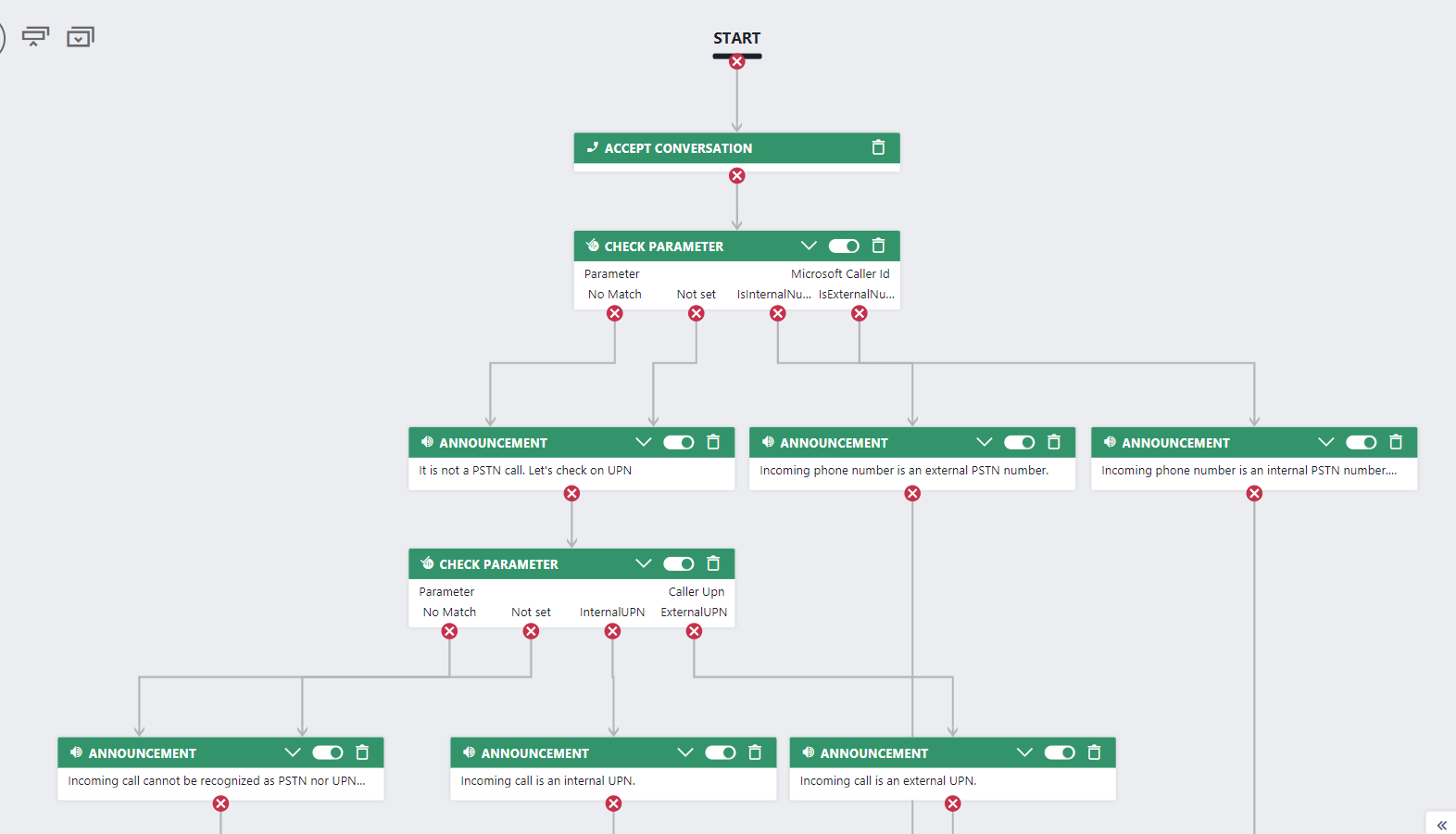
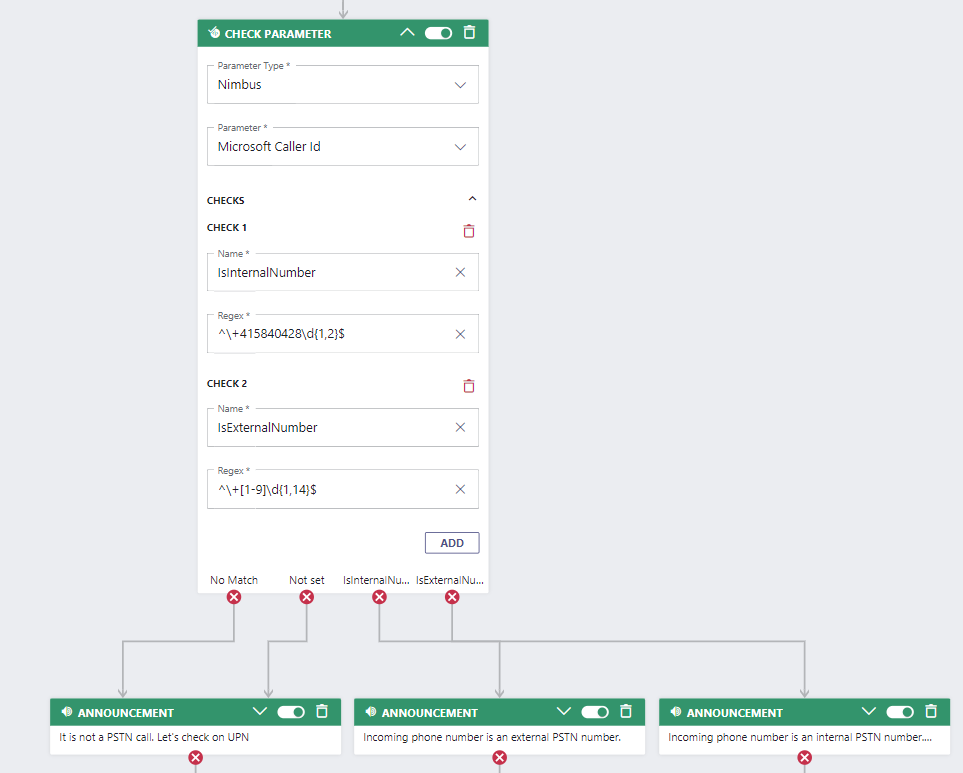
The first part of the flow validates the incoming call against a PSTN regular expression. Add a Check Parameter activity to the workflow and set it up as follows:
Checks
Note that in the activity we want to validate from specific (internal) to less specific (external). This means the order of the "Checks" matters, as the first successful match determines the exit taken in the activity |
|
|
Next we want to route the outcomes "IsInternalPSTN" and "IsExternalPSTN" to the specific services accordingly. If you want to handle anonymous calls in a special case, you can add the check-case like this:
|
|
Finally, we want to route the outcomes "No Match" or "Not set" to the next Check Parameter activity which validates the incoming call against a UPN regular expression.
Again, keep in mind to validate from specific to less specif ic.
|
 |
Test your workflow
- Assign the workflow to your service via the Modalities Service Settings.
- Call the service both internally via Teams (UPN) and externally (PSTN) to test the validation.
- To test the anonymous case, you can use your private mobile number and enable the number suppression mode of your mobile network provider. (For instance, call to +41432169346 *31# will suppress your number if you are calling with swisscom.)